Synapses And The 5 Most Important Neurotransmitters

Chemical Messengers Of The Brain
Neurotransmitters are messengers derived from chemicals that allow neurons to communicate with one another. Transmitting information between neurons enables them to work together as one unit by carrying data from one neuron’s axon (the output part of a neuron) to another neuron’s dendrite (the input part of a neuron). They get released from the presynaptic neuron and then bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron. The signals sent create electrical impulses in our brains.
Each neurotransmitter has a unique, defined role in regulating mood and behavior. Without neurotransmitters, neurons couldn’t send signals efficiently or accurately. In this blog post, we’ll break down five of the most important neurotransmitters in our bodies. Understanding these five will give you better insights into how your brain works and explain what they do.
1. Acetylcholine (ACh):
Known as the “classic” neurotransmitter. It was one of the first neurotransmitters discovered. It’s involved in many processes, such as
- Muscle Contraction
- Learning
- Memory
- Sleep Regulation
Acetylcholine imbalances have been linked to conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s
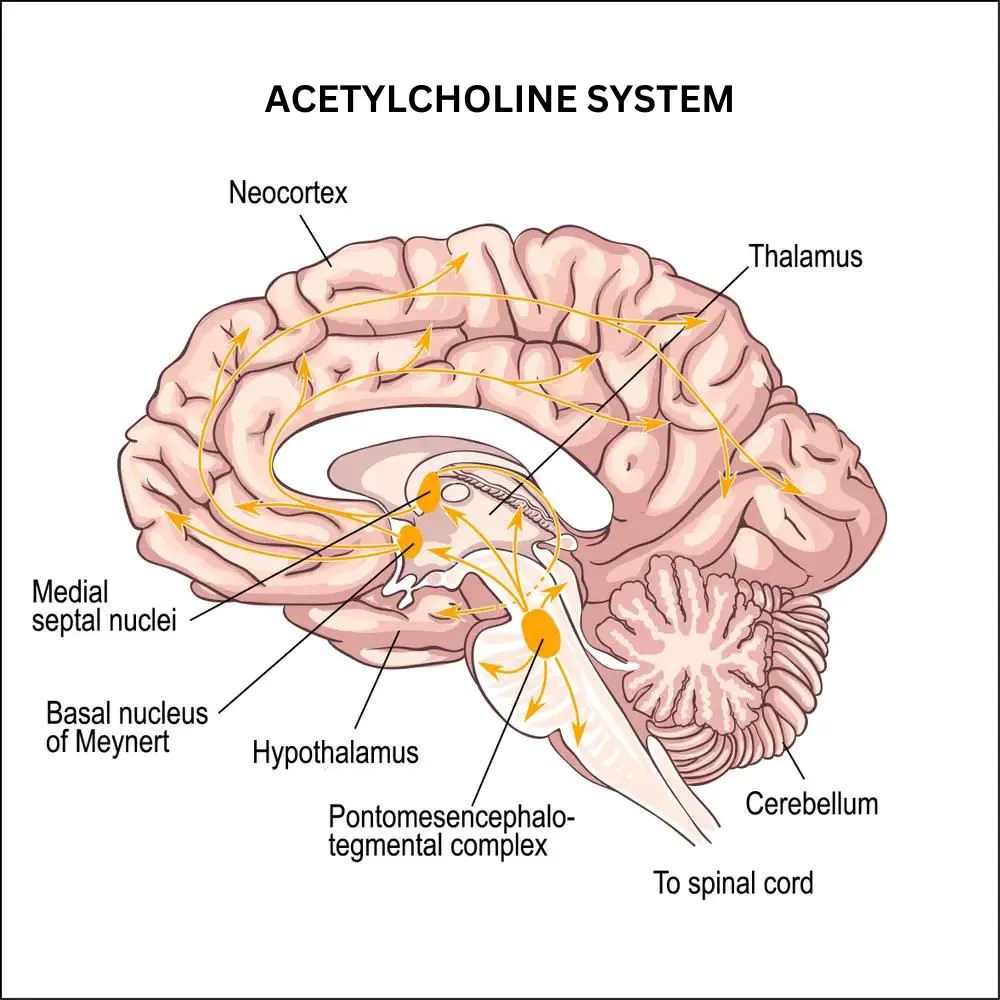
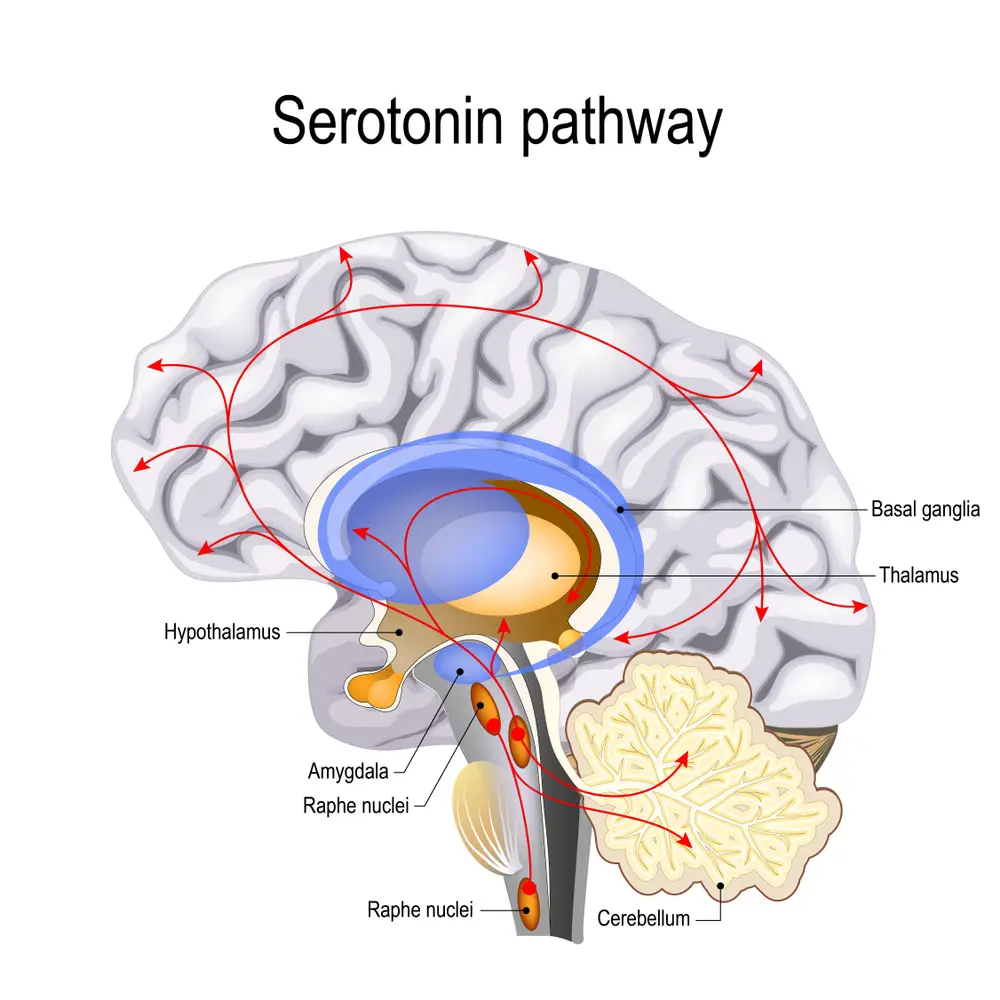
2. Serotonin (5-HT):
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter involved in mood regulation linked to conditions like depression and anxiety. It is also known to regulate appetite, sleep cycles, and body temperature. Low levels of Serotonin are linked to an increased risk of suicide.3. Dopamine (DA):
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter associated with motivation and reward-seeking behaviors. Low levels of dopamine are linked to attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) as well as addiction disorders such as substance use disorder, alcoholism, and gambling disorder.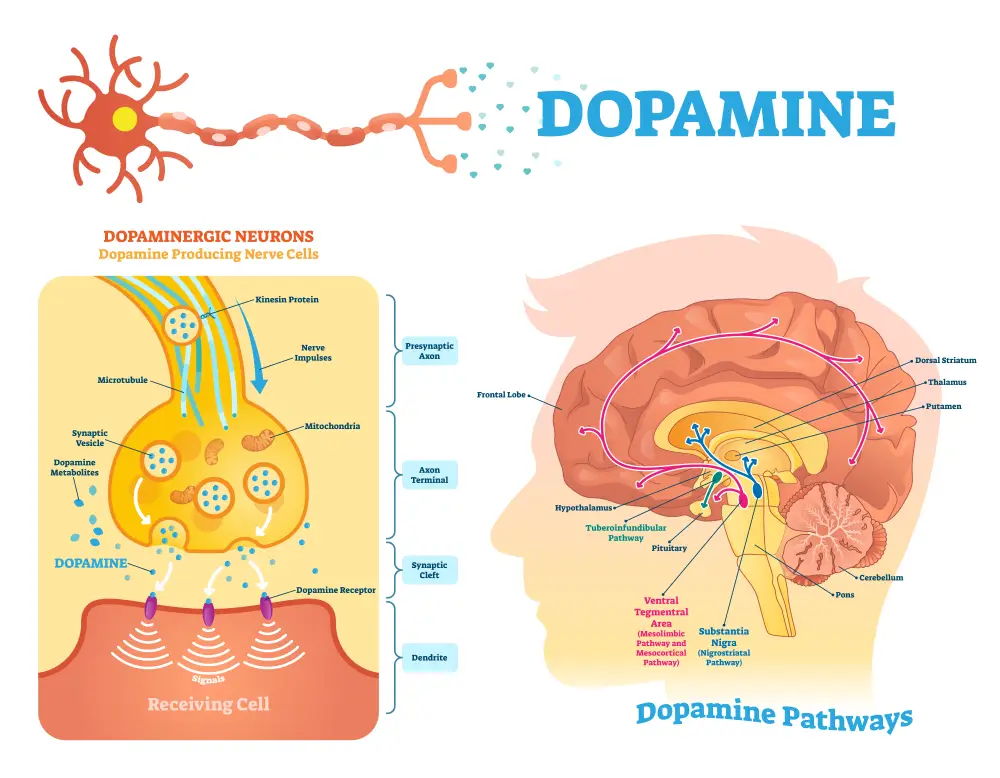
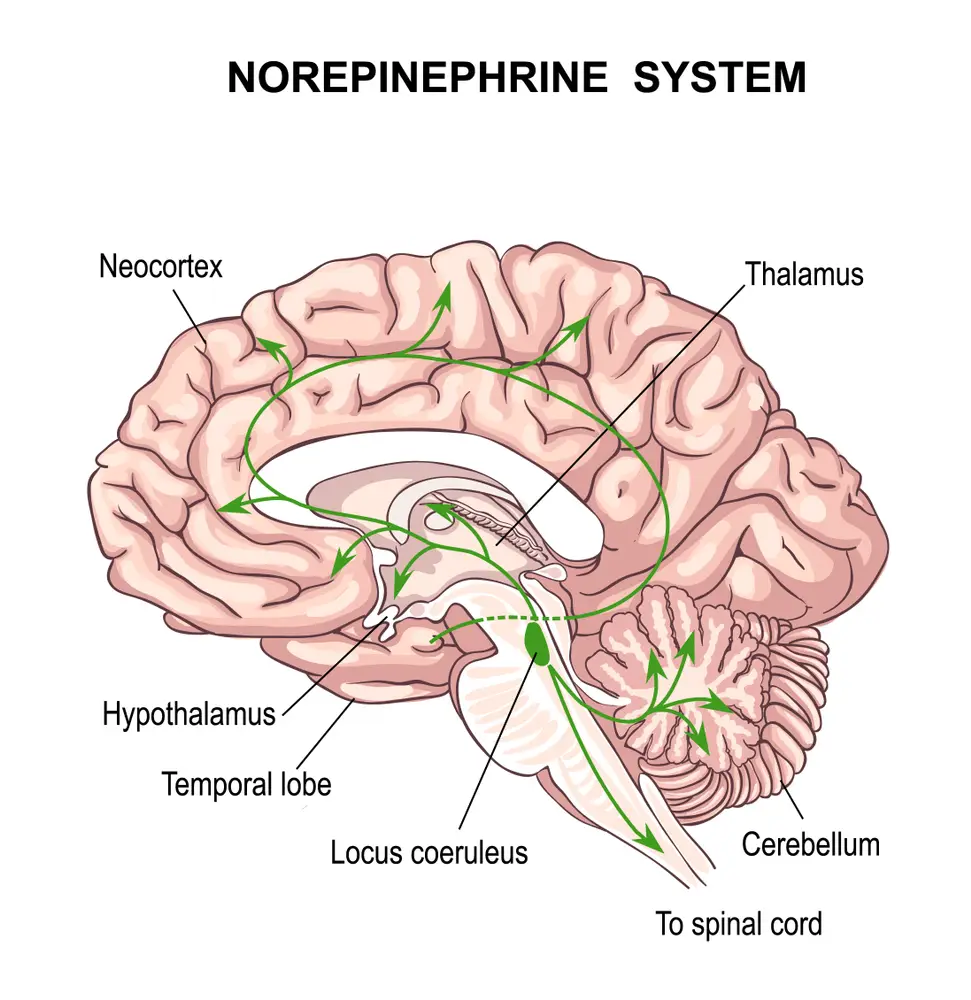
4. Norepinephrine (NE):
Norepinephrine is involved in alertness, arousal, focus, attention span, sleep cycles, and decision-making abilities. Low levels of norepinephrine causes fatigue, and high levels are associated with anxiety disorders such as panic disorder (PD) or generalized anxiety disorder (GAD).5. Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA):
GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter responsible for regulating excitatory activity in the brain. Low levels of GABA can lead to seizures or convulsions. High levels lead to sedation or relaxation effects due to their calming properties on the nervous system.
Learning about neuroscience can be exciting but overwhelming, so take your time understanding each concept thoroughly before moving on to new topics.
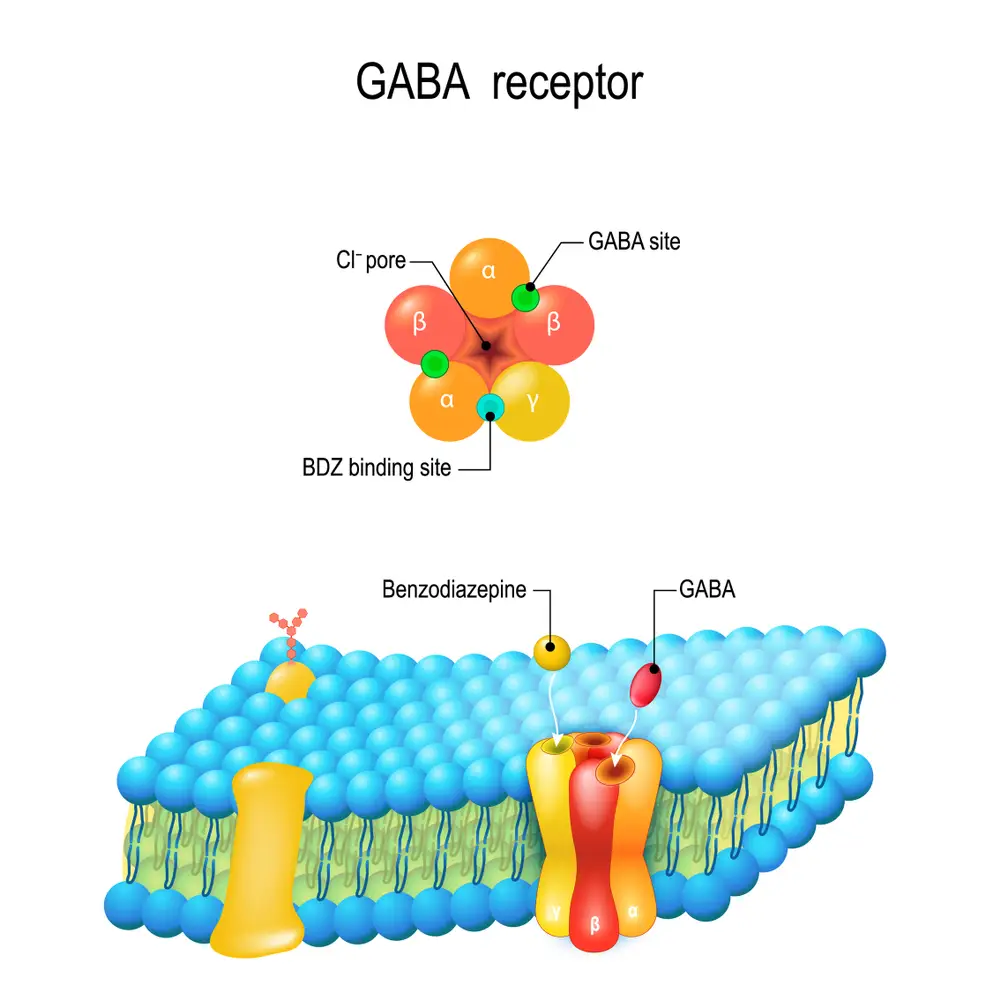
Overview Of Neurotransmitters And Synapses In The Brain
Have you ever wondered how your brain could send signals from one neuron to another? Probably just now. It all comes down to neurotransmitters and synapses. Let’s explore how these two components work together to keep our brains functioning.
Each type of neurotransmitter is responsible for different functions in the brain, such as regulating mood and controlling reward pathways. For example, dopamine is involved in reward-based learning, while Serotonin helps regulate mood and behavior.
Neurotransmitters are essential for our body’s functioning because they affect everything from emotions to physical movements.
How Neurotransmitters Work
They act as messengers in the brain, sending information from one neuron to another and distributing messages throughout the body. These neurotransmitters work correctly and efficiently in a healthy brain to promote communication between neurons. An imbalance in the amount or type of neurotransmitter present can disrupt communication between neurons and lead to mental health issues, feelings, or irregularity.
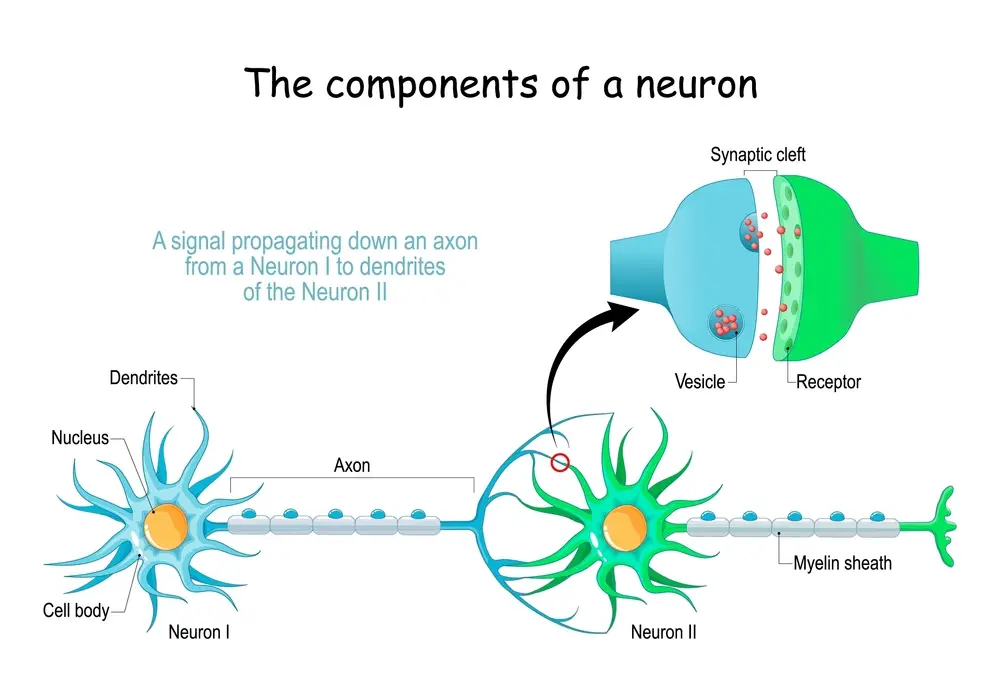
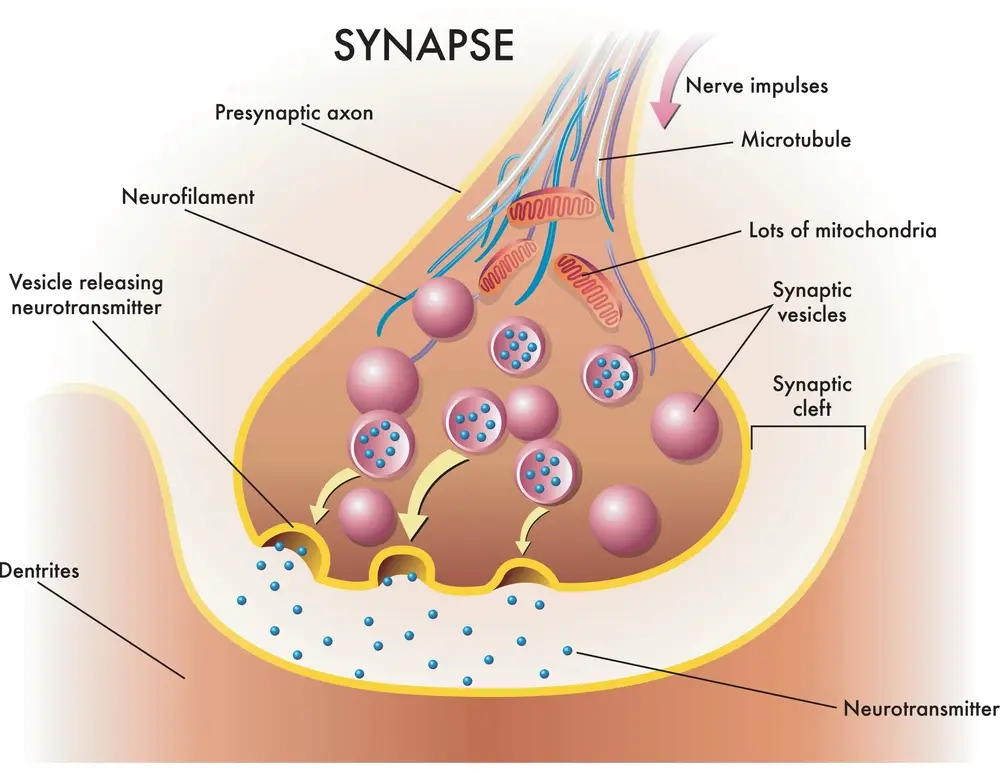
What are Synapses?
Synapses are the structures that allow neurons to communicate with each other by transferring electrical or chemical signals known as impulses. When a message reaches the end of a neuron’s axon, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters into what is known as the synaptic cleft, a tiny gap between two adjacent neurons. The neurotransmitter then binds to receptors on the adjoining neuron’s dendrite, which causes a change in its electrical charge, sending information from one neuron to another.
Synapses may be either excitatory or inhibitory, depending on their signal type. Excitatory signals cause neurons to fire, and inhibitory signals prevent them from firing. Personal experiences can also transform synapses. When an impulse travels through a particular synapse often enough, it will become more robust and efficient at transmitting signals over time. This process helps us learn new behaviors and form memories.
Factors that Cause a Neurotransmitter Imbalance
- Genetics
- Age-related changes in the brain
- Trauma/stressful events
- Diet/poor nutrition
- Medication side effects
- Substance abuse
- Physical and medical condition
These factors can all impact the neurotransmitters in the brain, which may lead to mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, or debilitating pain.
What Happens To Neurotransmitters In Mental Health Disorders?
Mental health is a complex topic, and understanding how the brain works is essential to learning more about disorders such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder. Depression causes chemical imbalances. Neurotransmitters are an integral part of this equation.

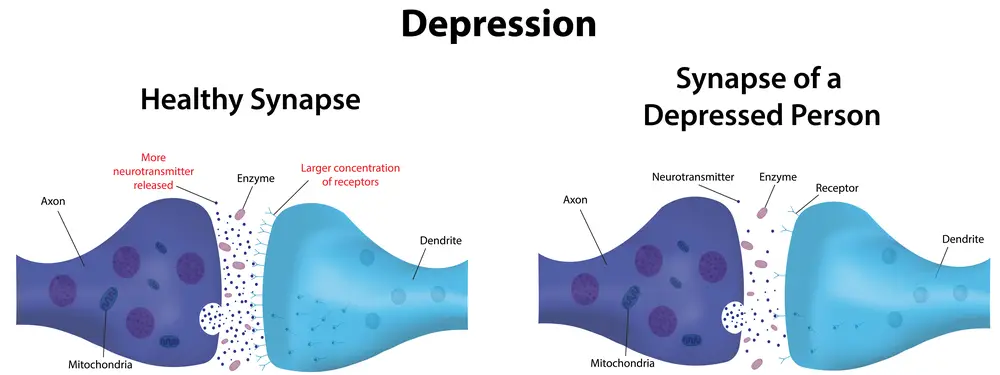

How Do Neurotransmitters Affect Depression?
The causes of depression vary, but researchers believe it has to do with neurotransmitters in the brain. When someone suffers from depression, there is usually an imbalance of neurotransmitters in their brain. Some research suggests people with depression have lower serotonin levels than those without it.
- Low serotonin levels correlate to feeling sad, tired, and having difficulty feeling pleasure or motivation. Coincidentally they are all common symptoms of depression, sadness, and fatigue.
- Studies have found that low levels of dopamine may also play a role in causing depression by making it difficult for people to feel pleasure or motivation.
- Recent research published in Molecular Psychiatry by University College London saw inconclusive evidence that low serotonin levels caused depression. The topic is certainly up for debate.
- Balancing neurotransmitters is essential in treating mental health disorders like depression or PTSD. They have a significant role in treating chronic pain as well.
By understanding how neurotransmitters affect depression, we can better equip ourselves with how best to manage our mental health.
Treatment For Neurotransmitter Imbalances
- The solution for neurochemical imbalances will depend on what caused them in the first place. Medication such as antidepressants which can help regulate serotonin and dopamine levels, or mood stabilizers may be prescribed by your doctor if necessary.
- Lifestyle changes such as improving your diet or exercise activity could help improve symptoms associated with mental health disorders.
- Therapy can be beneficial for managing symptoms associated with neurochemical imbalances and addressing any underlying causes that might be contributing to them.


Mental Health Therapy For Neurotransmitter Imbalances
Numerous therapy options are available, like medication, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), meditation, yoga, and other forms of exercise. They may improve these imbalances and reduce symptoms associated with neurotransmitter imbalances. More aggressive treatment may be necessary if the illness is severe, like prescription medications or ketamine therapy.
Talk With A Mental Health Practitioner
Talking with a mental health practitioner can help address negative thought patterns associated with depression and provide coping skills for managing symptoms.
- Exercise can boost endorphin production, improve mood and reduce stress levels associated with depression.
- Balancing Neurotransmitters plays a critical role in treating mental health disorders. They even have a significant role in treating chronic pain.
So there you have it;
- Neurotransmitters and synapses work together for our brains to function correctly.
- Neurotransmitters help transfer information from one neuron to another. At the same time, synapses facilitate this communication by carrying electrical or chemical impulses across tiny gaps called synaptic clefts. These two components play a crucial role in our everyday lives. They can also be altered by experiences, which help us learn new behaviors and form long-term memories.
- Understanding how these two components work together gives us insight into how our brains process information our why we behave the way we do.
In conclusion, learning how neurotransmitters work is paramount when discussing mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, or PTSD. Neurotransmitters are responsible for sending messages that communicate throughout the body. They can become imbalanced due to various factors, which may cause disruptions in the communication between neurons leading to mental health issues or pain. Treatment for neurochemical imbalances can vary depending on what caused them. It may include medication or lifestyle changes like improving your diet or exercising more often.
Remember, everyone’s experience with mental health disorders is different. What might work for you might not work for someone else works for some people and might not work for others. It’s always best to do your due diligence and discuss the available options with your healthcare provider before making any changes or decisions about treatment.

Article Reviewed By

Richard Koffler, MD
NPI Number- 1467557264
- Dr. Koffler is a Physiatrist, specializing in Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation.
- Graduated from the Sackler School of Medicine at Tel Aviv University in 1993 Dr. Koffler completed a one-year internship in internal medicine at Roosevelt Hospital in New York City.
- Residency in Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation at the Rusk Institute at NYU Medical Center in New York City. Board certified in 1998.
- Trained in acupuncture at Helms Medical Institute at UCLA His medical practice incorporates proven conventional western medicine integrating eastern alternative practices.
- Medical Director of several medical clinics in NYC, Stamford CT, and Miami Beach, FL.
Medical Disclaimer
The information on this site is not intended or implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. All content, including text, graphics, images, and information, contained on or available through this website is for general information purposes only. Ketamine DRS makes no representation and assumes no responsibility for the accuracy of the information contained on or available through this website, and such information is subject to change without notice. You are encouraged to confirm any information obtained from or through this website with other sources and review all information regarding any medical condition or treatment with your physician.
NEVER DISREGARD PROFESSIONAL MEDICAL ADVICE OR DELAY SEEKING MEDICAL TREATMENT BECAUSE OF SOMETHING YOU HAVE READ ON OR ACCESSED THROUGH THIS WEBSITE.

