Understanding Neuroplasticity: How The Brain Rewires Itself And How Ketamine Helps The Process

What Is Neuroplasticity?
Neuroplasticity is a term used to describe how our brains can reorganize and form new neural pathways. That means our brains can adapt and change, even as we age. In case you are wondering, even as we age, neuroplasticity occurs.
Neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s ability to adapt and change, responding to new information or experiences in response to stimuli, and environmental or physical conditions, such as learning a new skill or recovering from an injury. It does this by reorganizing neuronal connections in response to environmental or physical conditions changes enabling us to learn new skills, adjust to different environments, develop new habits and remember information or processes for years.
Let’s dive deeper into neuroplasticity, how it works, and why it is essential to living our best lives.

When the brain forms new connections between neurons, it increases the efficiency of communication between them. This process happens throughout life but becomes particularly important during childhood development as we find our way in the world.
As we go through life, our brains constantly reshape themselves based on experience and environment, allowing us to adapt more efficiently over time. Human beings’ biggest distinction from other animals and part of the reason human evolution is because of our ability to adapt to change.
How Does Neuroplasticity Work?
Neuroplasticity works by forming new connections between neurons or strengthening existing ones. When the brain becomes more efficient at processing information and responding to various environmental stimuli, the response to trauma or stress triggers can be somewhat mitigated. For example, suppose you practice a skill over a long period. In that case, your brain will form more robust connections between neurons related to that skill, allowing you to perform better in that area. Thats why “repetition is the mother of skill.” Repeating tasks helps create stronger new neural connections for learning activities such as reading or playing an instrument.
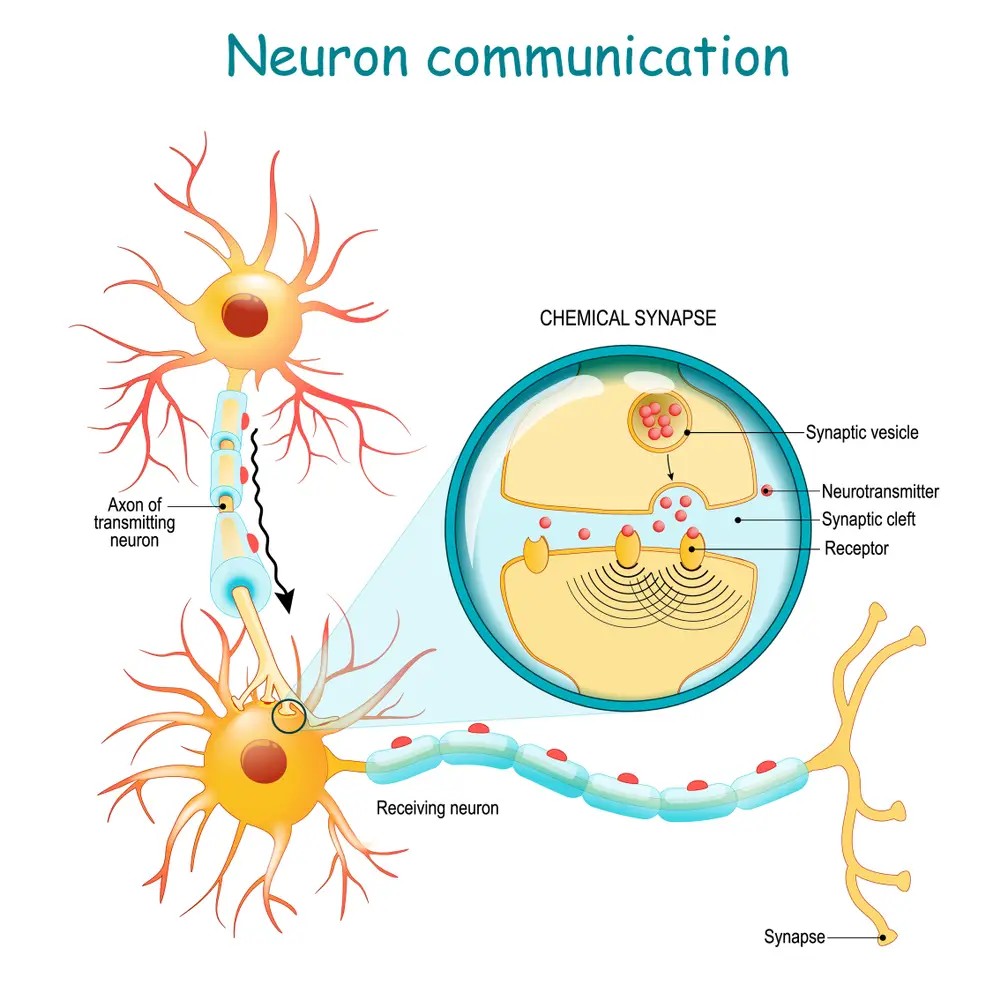

Why Is Neuroplasticity Important?
Neuroplasticity is essential because it allows us to change our perceptions and unique circumstances to have a new outlook on life. Sometimes it leads us to change our environments, develop adaptive behaviors and create new habits that better suit our current situation.
Researchers believe neuroplasticity may be instrumental in treating certain neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer’s or Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), by giving scientists insights into how it affects the brain’s functioning.
How Does Ketamine Promote Neuroplasticity?
- Ketamine’s effect on neuroplasticity is related to its action on the glutamate system in the brain.
- Glutamate is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that helps regulate neuronal activity.
- When ketamine binds to glutamate receptors, it blocks their activity.
- It causes a decrease in neuronal firing, which increases the likelihood of new connections formed between neurons.
- This increased synaptic plasticity leads to enhanced learning and memory formation, improving mood regulation and emotional control over time.
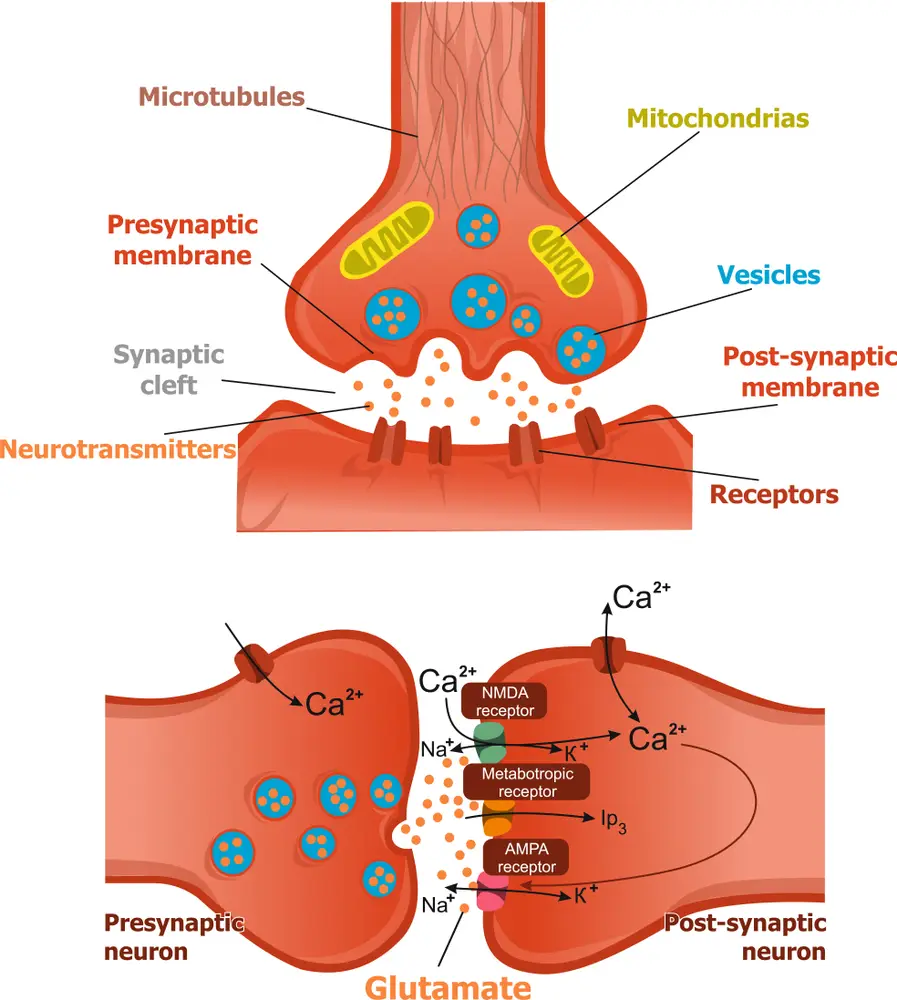

The Role Of Glutamate In Neuroplasticity
- Ketamine interacts with glutamate receptors in the brain, which are critical for learning and memory.
- Glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter that helps neurons communicate with each other.
- It is also associated with long-term potentiation (LTP), the process by which memory formation occurs.
- Studies have shown that ketamine increases glutamate receptor activity, which can lead to increased neuroplasticity.
Ketamine’s Impact On Neurogenesis
The “ketamine effect” on the brain has been studied for over 70 years and FDA-approved for over 50 years. Still, it’s only recently that scientists have begun to explore how ketamine may influence neuroplasticity. The brain’s ability to reorganize neuronal connections when attention is directed toward an outcome expedites change and promotes new paths to travel down.
Let’s examine how ketamine affects neuroplasticity and why it may benefit specific medical conditions.


With the proper treatment and mindfulness, our brains can “rewire” themselves by forming these new neural connections (synapses) between neurons. This process is essential for learning and memory formation. Understanding how ketamine causes neuroplasticity can help us better understand why it works as a mental health treatment.
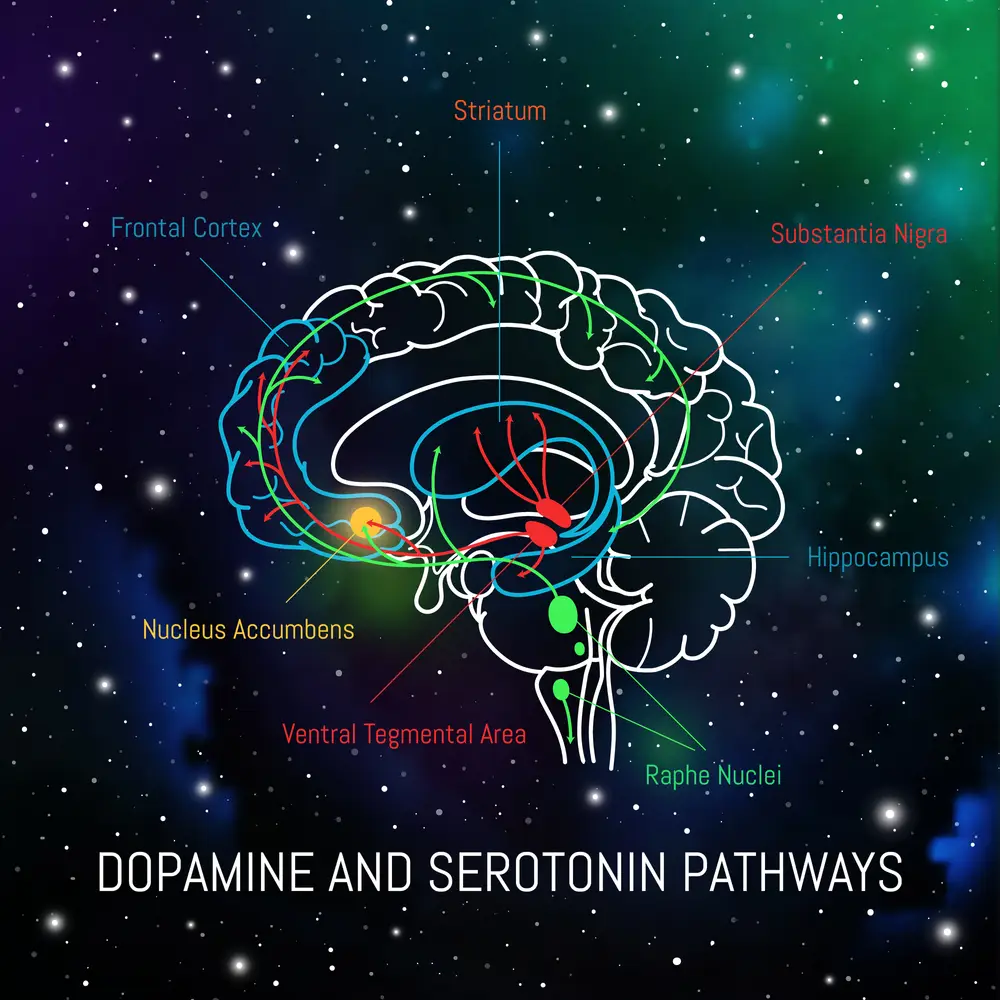
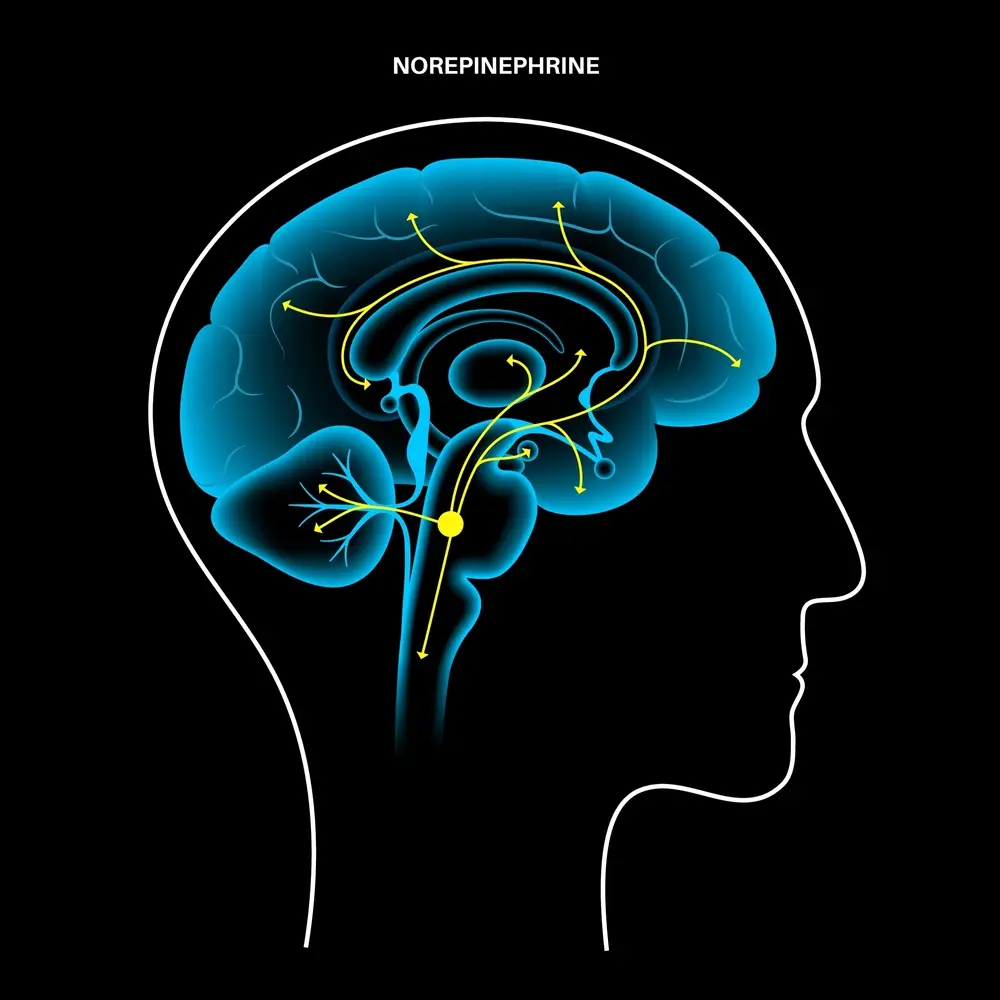
Modulation Of Neurotransmitters With Ketamine
Ketamine modulates the release of other neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin, which are linked to mental health disorders like depression and anxiety. By influencing these chemicals, ketamine may be able to address some underlying contributing factors that are associated with mental health issues.
Ketamine is a medication that has been used for decades as an anesthetic in medical settings. Still, it has recently gained greater recognition as a mental health treatment. Studies have shown that ketamine can effectively treat depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders, but how does it work? The answer lies in its ability to cause neuroplasticity.
Ketamine’s Effects On Depression
One of the most well-known effects of ketamine is its ability to reduce symptoms of depression. It’s attributed to its affecting serotonin levels in the brain. Recent research suggests that ketamine’s impact on neuroplasticity may also play a role.
Studies have found that antidepressant medications like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) activate specific pathways in the brain involved in neuroplasticity. That suggests that antidepressants may also influence these processes.
Rewiring The Brain
Neuroplasticity is an amazing phenomenon that allows our brains to rewire themselves based on experience and environment. The process can profoundly affect our lives from childhood development through adulthood. By understanding neuroplasticity more deeply, scientists can make great strides in treating neurological disorders. At the same time, everyday people can use knowledge of this concept to improve their cognitive abilities over time by utilizing targeted learning activities such as reading or practicing an instrument regularly. Neuroplasticity is an incredible tool that can help everyone reach their full potential.

How Does Ketamine Affect Neuroplasticity, And Why It May Be Beneficial For Specific Medical Conditions?
Overall, we still don’t know much about all the impacts ketamine has on neuroplasticity and the potential benefits for specific medical conditions like depression or anxiety disorder. However, what we do know is encouraging. It appears that ketamine affects particular pathways involved in learning and memory formation and promotes new neuron growth, potentially improving cognitive functioning over time. As research continues into this area, we may uncover more ways ketamine could help those suffering from mental health issues, chronic pain, or other neurological disorders.
The evidence supporting ketamine’s ability to cause neuroplasticity is mounting every day. We are learning more about how this powerful drug works on both a physiological and psychological level. More research is needed to understand how ketamine treats mental health disorders clinically. The potential for improving our understanding of neuroplasticity can dramatically impact mental health treatments. In addition, understanding how ketamine works could lead us closer to finding effective treatments for depression and other mood disorders without relying solely on pharmaceuticals.
If you or someone you know is struggling with mental health issues, talk with your doctor about whether ketamine might be right for you.
Article Reviewed By

Richard Koffler, MD
NPI Number- 1467557264
- Dr. Koffler is a Physiatrist, specializing in Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation.
- Graduated from the Sackler School of Medicine at Tel Aviv University in 1993 Dr. Koffler completed a one-year internship in internal medicine at Roosevelt Hospital in New York City.
- Residency in Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation at the Rusk Institute at NYU Medical Center in New York City. Board certified in 1998.
- Trained in acupuncture at Helms Medical Institute at UCLA His medical practice incorporates proven conventional western medicine integrating eastern alternative practices.
- Medical Director of several medical clinics in NYC, Stamford CT, and Miami Beach, FL.
Medical Disclaimer
The information on this site is not intended or implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. All content, including text, graphics, images, and information, contained on or available through this website is for general information purposes only. Ketamine DRS makes no representation and assumes no responsibility for the accuracy of the information contained on or available through this website, and such information is subject to change without notice. You are encouraged to confirm any information obtained from or through this website with other sources and review all information regarding any medical condition or treatment with your physician.
NEVER DISREGARD PROFESSIONAL MEDICAL ADVICE OR DELAY SEEKING MEDICAL TREATMENT BECAUSE OF SOMETHING YOU HAVE READ ON OR ACCESSED THROUGH THIS WEBSITE.



